Microsoft Access is a powerful and versatile database management system that can be used to create an efficient and user-friendly drawing register for engineers, construction consultants, and manufacturing organisations. A well-structured Access database can provide a robust solution for managing drawings, revisions, and changes, and allow for multiple users to collaborate and access the register. In this article, we will outline the basic structure of a Microsoft Access based drawing register, including the types of tables, input screens, and reporting screens that can be created.
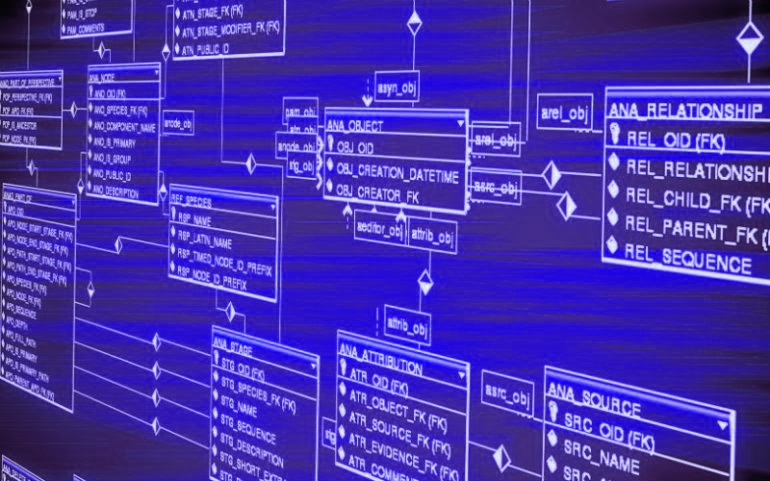
Tables: The foundation of any Access database is its tables. Tables in an Access drawing register can be used to store different types of information, such as project details, drawing information, revision history, user accounts, and more. For example, a “Projects” table can store information related to various projects, including project names, project numbers, and project statuses. A “Drawings” table can store details about individual drawings, such as drawing numbers, revision numbers, drawing titles, and drawing file paths. A “Revisions” table can store the revision history of each drawing, including revision numbers, revision dates, and revision descriptions. Properly structuring the tables in the database is crucial to ensure data integrity and efficient retrieval of information.
Input Screens: Access allows for the creation of user-friendly input screens that allow users to enter and edit data in the tables. Input screens can be designed to capture relevant information about drawings, projects, revisions, and other related data. For example, a project input screen can include fields for entering project details such as project name, project number, and project status. A drawing input screen can include fields for entering drawing information such as drawing number, title, and file path. Revision input screens can include fields for entering revision details such as revision number, date, and description. These input screens can be designed with data validation rules and input masks to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
Reporting Screens: Access provides powerful reporting capabilities that can be used to generate various types of reports for analysis and decision-making. Reporting screens in an Access drawing register can be designed to provide insights and summaries of the drawing data stored in the database. For example, a drawing register report can provide a list of drawings sorted by project, drawing number, or revision status. A revision history report can provide a detailed list of revisions for each drawing, including revision numbers, dates, and descriptions. These reports can be designed with filters and sorting options to allow users to customise the view of the data according to their requirements.

User Accounts: Access allows for the creation of multiple user accounts with different levels of access and permissions. This feature can be utilised to manage user access to the drawing register, ensuring that only authorised users can view, edit, or delete data in the database. User accounts can be created with different security levels, such as read-only access, read-write access, or administrator access, depending on the role and responsibilities of each user. This helps maintain data integrity and security of the drawing register.
A well-structured Microsoft Access based drawing register can provide an efficient and user-friendly solution for managing drawings, revisions, and changes in engineering, construction, and manufacturing industries. Properly designed tables, input screens, reporting screens, and user accounts can ensure data integrity, security, and accessibility for multiple users. Access provides a flexible and customisable platform for creating a drawing register that meets the specific requirements of different organisations.